A comprehensive guide to understanding psoriasis, its various types, symptoms, and evidence-based treatment options.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition affecting approximately 2-3% of the global population. This condition accelerates skin cell production, causing cells to build up rapidly on the surface. The result? Patches of thick, red skin covered with silvery scales that can be both uncomfortable and distressing.
Key Facts About Psoriasis:
- Affects 2-3% of people worldwide
- Chronic autoimmune condition
- Causes rapid skin cell turnover
- Not contagious
- Can appear at any age
5 Main Types of Psoriasis
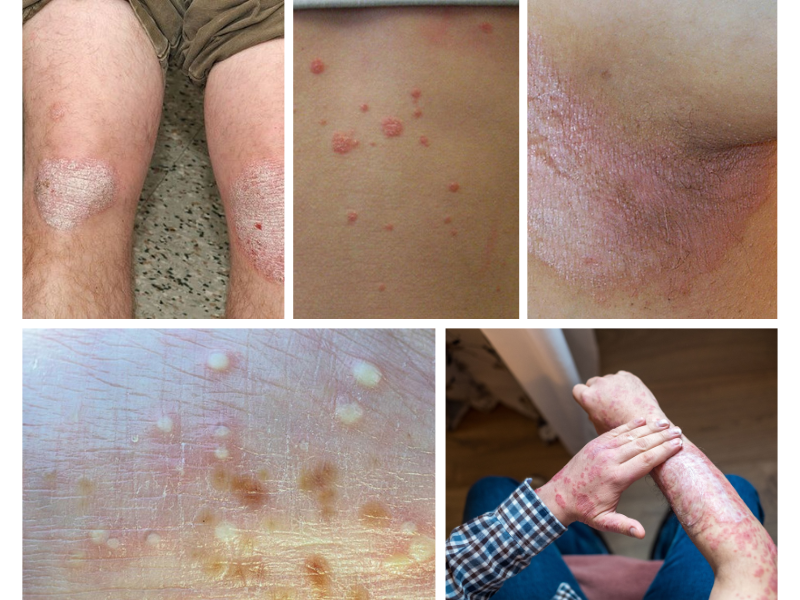
1. Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris)
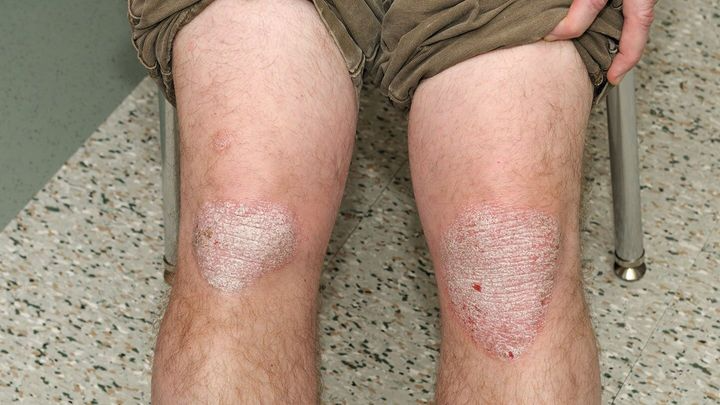
Most Common Form (80-90% of cases)
- Characteristics: Raised, red patches with silvery-white scales
- Common locations:
- Scalp
- Elbows
- Knees
- Lower back
2. Guttate Psoriasis

- Appears as small, drop-shaped lesions
- Often triggered by strep infections
- Most common in children and young adults
3. Inverse Psoriasis

- Appears in skin folds
- Characteristics:
- Smooth, red patches
- Lacks typical scaling
- Areas affected:
- Under breasts
- Groin
- Armpits
4. Pustular Psoriasis
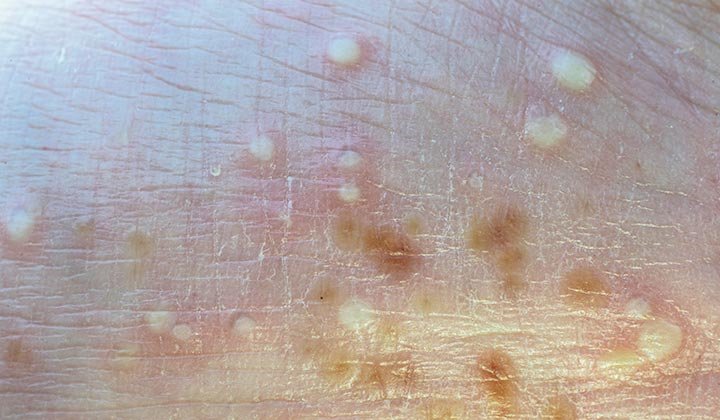

- White pustules surrounded by red skin
- Can be localized or widespread
- Requires immediate medical attention if widespread
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
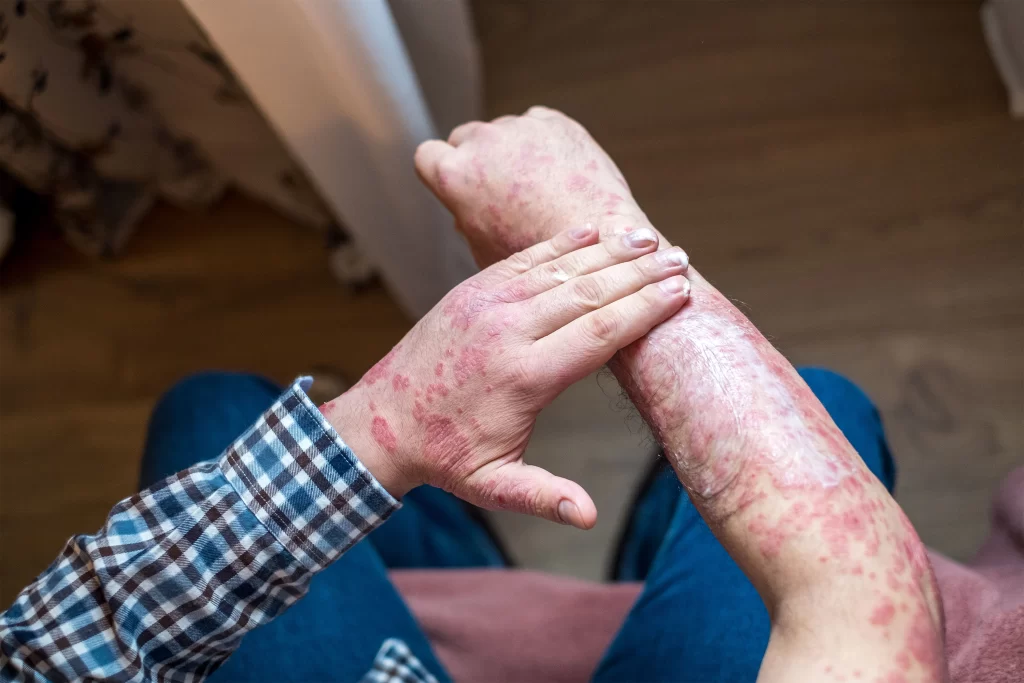
- Rare but severe form
- Causes widespread redness and scaling
- Medical Emergency: Requires immediate treatment
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis
- Red, inflamed skin patches
- Silvery-white scales
- Itching and burning
- Dry, cracking skin
- Bleeding points when scales are removed
- Nail changes (pitting, ridges)
- Joint pain (in psoriatic arthritis)
Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
- Family history increases risk
- Certain genes linked to psoriasis
Environmental Triggers
- Stress
- Skin injury
- Infections
- Medications
- Weather changes
Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Poor diet
Understanding Psoriasis Triggers
Common Triggers to Avoid
Infections
- Strep throat
- Upper respiratory infections
- Skin infections
Medications
- Lithium
- Beta-blockers
- Antimalarial drugs
Environmental Factors
- Cold, dry weather
- Skin injuries
- Excessive sun exposure
Lifestyle Factors
- High stress levels
- Alcohol consumption
- Smoking
- Poor sleep habits
Serious Complications of Psoriasis
Physical Complications
Psoriatic Arthritis
- Affects up to 30% of patients
- Can cause permanent joint damage
- Early treatment is crucial
Cardiovascular Disease
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Higher stroke risk
- Regular screening recommended
Metabolic Syndrome
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
Mental Health Impact
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Social isolation
- Self-esteem issues
Treatment Options
1. Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids
- Vitamin D analogs
- Coal tar preparations
- Moisturizers
2. Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
- UVB light treatment
- PUVA therapy
- Excimer laser
3. Systemic Medications
- Traditional Systemics:
- Methotrexate
- Cyclosporine
- Acitretin
- Biologics:
- TNF-alpha inhibitors
- IL-17 inhibitors
- IL-23 inhibitors
4. Lifestyle Modifications
- Stress management
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Adequate sleep
FAQs About Psoriasis
Is Psoriasis Contagious?
No, psoriasis cannot be transmitted from person to person. It’s an autoimmune condition triggered by internal factors.
Can Diet Affect Psoriasis?
Yes, diet can impact psoriasis severity. Anti-inflammatory foods may help:
- Omega-3 rich fish
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Limited processed foods
How Long Do Flares Last?
Flares can last weeks to months, varying by:
- Treatment effectiveness
- Trigger management
- Individual factors
Can Children Get Psoriasis?
Yes, psoriasis can develop at any age, including childhood. Early diagnosis and treatment are important.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Widespread redness and scaling
- Joint pain with skin symptoms
- Severe itching or pain
- Signs of infection
- Impact on daily activities